
ArcBlock has launched the next phase of its strategic roadmap: ABT Convexity, a pioneering platform that merges decentralized blockchain with cloud computing. In an exclusive discussion with CryptoSlate, CEO Robert Mao and CTO Gness McKinney detailed the implications of this significant update.
ArcBlock is developing a comprehensive framework for connecting permissioned and permissionless blockchains, placing it in direct competition with prominent interoperability projects like Polkadot and Cosmos.
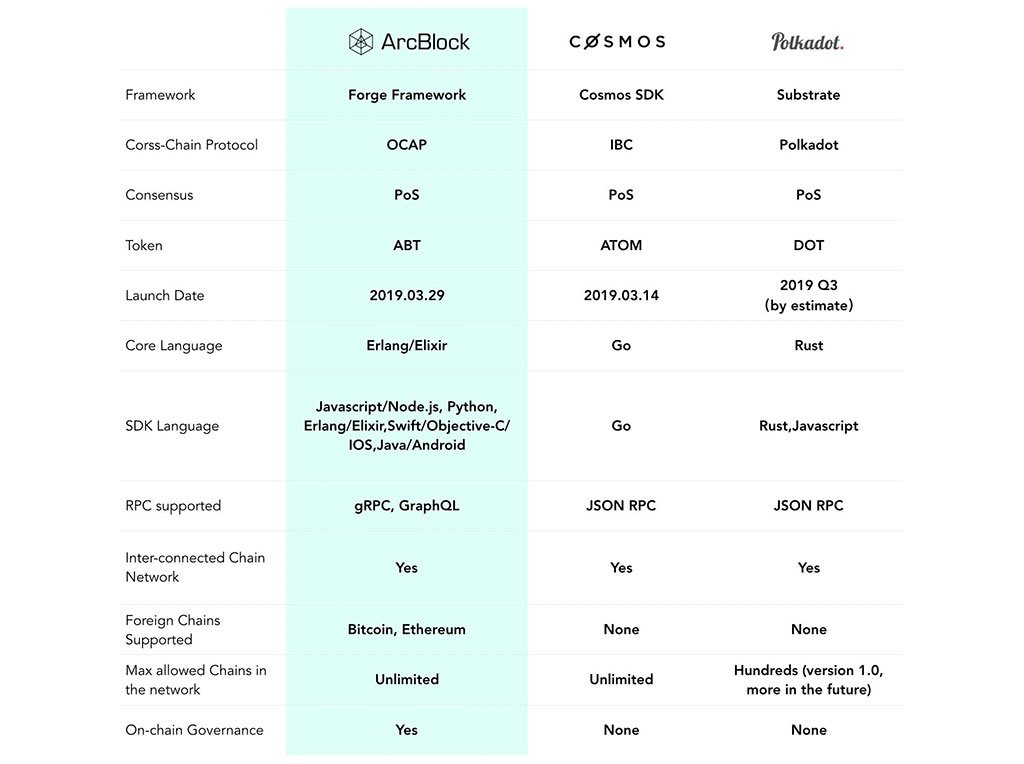
The Seattle-based company describes its platform as a 'Blockchain 3.0' ecosystem, enabling developers to build applications that seamlessly interact with major networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Hyperledger from a single, unified codebase. The network's core mission is to foster an environment of DApps that are interconnected, interoperable, and autonomous, free from centralized control.
The native utility token of the platform, ABT, is integral to the network, used primarily for granting access and facilitating transactions within the ArcBlock ecosystem.
According to McKinney, ABT Convexity is engineered to be the 'world's simplest blockchain node software.'
Traditionally, running a node has been a complex task, limited to technically proficient enthusiasts or large-scale, energy-intensive mining operations common in proof-of-work systems. Cryptocurrency mining is intentionally resource-intensive, with the computations from proof-of-work mining offering little value outside of securing the network.
Resources dedicated to securing the network are simultaneously leveraged to perform useful work, a feature enabled by a novel proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, as outlined in ArcBlock's technical documentation.
For those interested in participating in ArcBlock staking or learning more, explore the official resources here.
ArcBlock strategically leverages cloud computing infrastructure instead of traditional mining farms, providing users with the necessary resources to build and deploy DApps efficiently. The company asserts that its platform is the first capable of running AWS Spot instances in a fully decentralized manner.
These nodes operate without central hubs or controllers, a system ArcBlock describes as 'completely decentralized.' This architecture is achieved through the platform's proof-of-stake consensus, powered by the ABT token.
Allegedly, nodes deployed via this cloud framework are fault-tolerant, feature auto-upgrades, and are easily migratable. Moreover, they can be run locally, connected peer-to-peer, or deployed on a public network to offer online services.
ABT Convexity provides user-friendly infrastructure, enabling the use of low-cost servers like Digital Ocean's $15/month droplet to achieve 100 transactions per second (TPS) on the network—a significant leap over the ~15 TPS often seen on proof-of-work-based chains like Ethereum.
And, it seems major cloud companies are taking notice of this new framework. ArcBlock has so far secured partnerships with industry leaders including AWS, Google, Digital Ocean, Upyun, and others.
ArcBlock also recently joined the newly launched Cascadia Blockchain Council as a founding member. The council includes significant players in the Pacific Northwest's blockchain sector, such as telecom giant T-Mobile and Microsoft.
ABT Convexity holds significant promise. By enabling developers to build on top of agile blockchain protocols and access the required cloud resources seamlessly, ArcBlock could dramatically accelerate the pace of decentralized application development.
Learn more about ABT Convexity and the broader ArcBlock ecosystem.